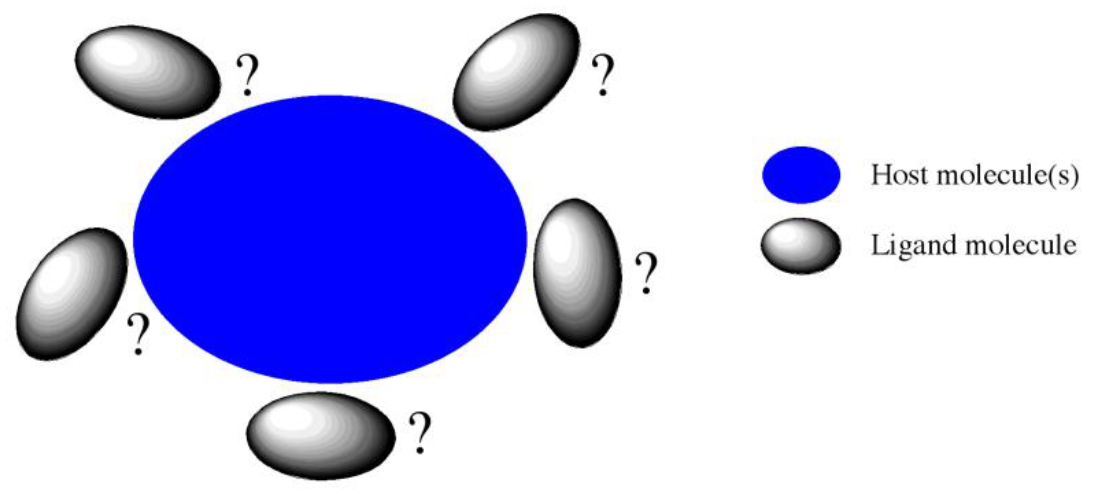
Host-Ligand coordination search
CONFLEX has a function called “Host-Ligand coordination search”. It is useful for finding stable structures of complex molecules or molecular clusters by exploring stable relative positions and orientations of a molecule to other molecule(s). In this search method, the molecule(s) are defined as “host”, and the other molecule or ionic species is defined as “ligand”. The ligand is arranged around th Host automatically (refer to the figure 1). This function can be expected to be applied to the supramolecular chemistry such as molecular recognition or host-guest chemistry.
[Overview of search method]
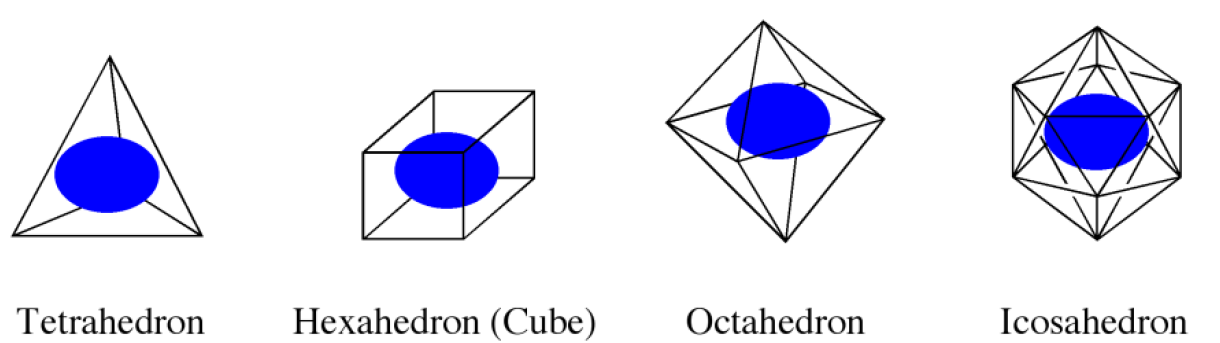
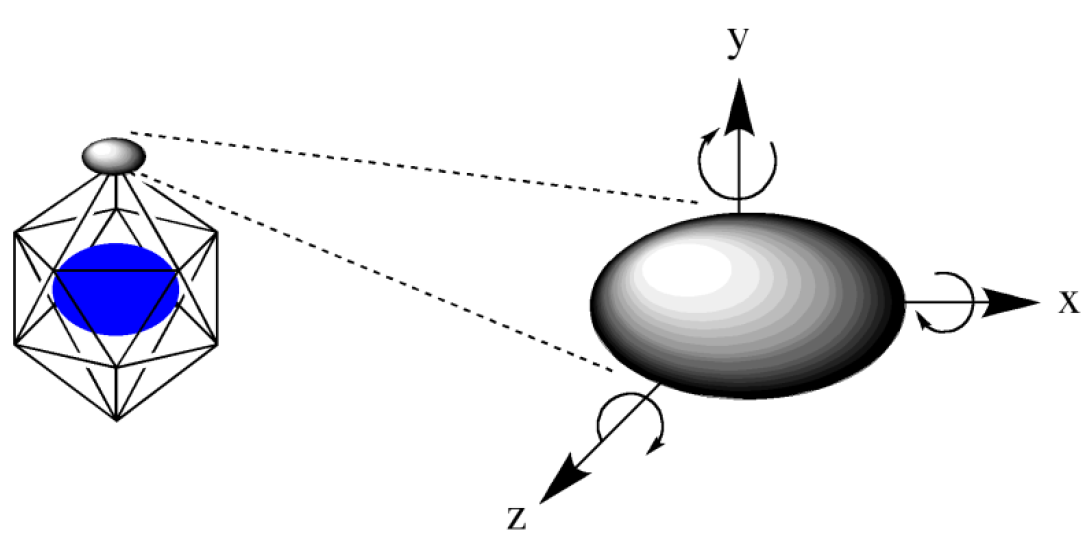
First, we choose a regular polyhedron surrounding the host molecule(s). CONFLEX supports 4 polyhedron models; tetrahedron, hexahedron, octahedron, and icosahedron (Figure 2). The icosahedron is used in the default setting.
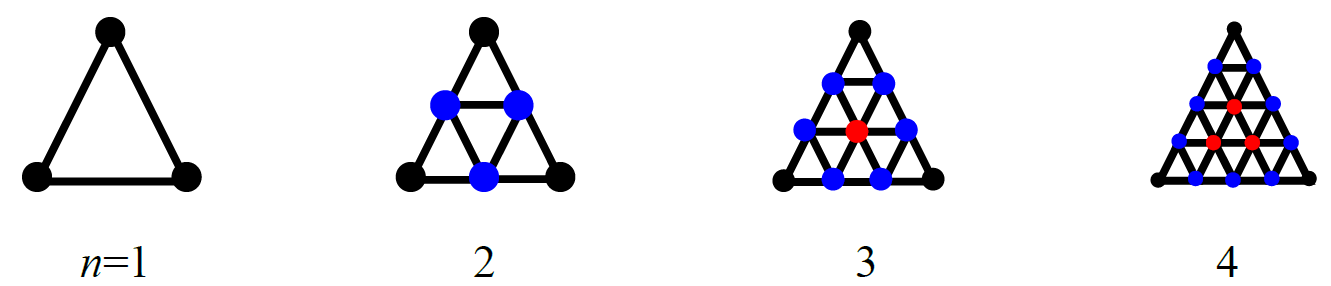
CONFLEX arranges the ligand molecule on the vertices of the regular polyhedron. If you want to explore stable structures in detail, you can increase the points for arranging the ligand by dividing each plane of the regular polyhedron by using “HLSEARCH_HOST_NDIV=n” keyword (Figure 3).
The ligand arranged is rotated around the x, y, and z axes to generate initial coordination structures (Figure 4). The initial structures are subjected to a geometry optimization and the optimized structures are outputted in order of energy. The angle of rotation can be specified by a keyword “HLSEARCH_LIGAND_ROT=(l,m,n)”, and the default setting is 60 degrees (l=m=n=6). When the keyword “HLSEARCH_LIGAND_ROT=(8,8,8)” is used, the rotation angle is set to 45 degrees.
[Stable coordinations of two acetic acid molecules]
This section applies the Host-Ligand coordination search to a molecular complex of two acetic acids.
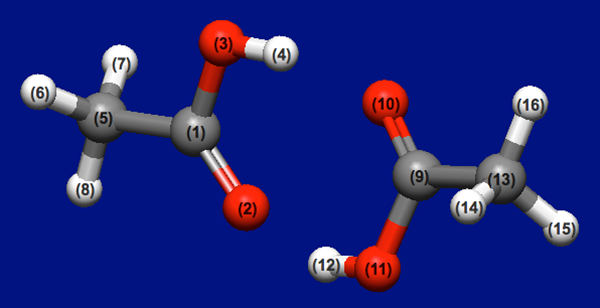
Structure data (acetic_acid_dimer.mol)
acetic_acid_dimer.mol
16 14 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0.9628 -0.5511 0.0000 C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2.1931 -0.5511 0.0000 O 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0.3335 0.6511 0.0000 O 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0.9803 1.3755 -0.0000 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-0.0286 -1.7296 0.0001 C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-0.6441 -1.6778 0.8738 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-0.6442 -1.6778 -0.8735 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0.5138 -2.6519 0.0000 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
3.5500 2.4393 0.3355 C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2.4107 2.2978 -0.1068 O 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.2100 1.3256 0.7422 O 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
3.6576 0.5365 0.6183 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.3924 3.7159 0.5151 C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4.6407 3.8369 1.5488 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5.2907 3.6344 -0.0604 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
3.8309 4.5636 0.1817 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 2 2 0 0 0 0
1 3 1 0 0 0 0
1 5 1 0 0 0 0
3 4 1 0 0 0 0
5 6 1 0 0 0 0
5 7 1 0 0 0 0
5 8 1 0 0 0 0
9 10 2 0 0 0 0
9 11 1 0 0 0 0
9 13 1 0 0 0 0
11 12 1 0 0 0 0
13 14 1 0 0 0 0
13 15 1 0 0 0 0
13 16 1 0 0 0 0
M END
[Execution by Interface]
Open the acetic_acid_dimer.mol file by CONFLEX Interface.
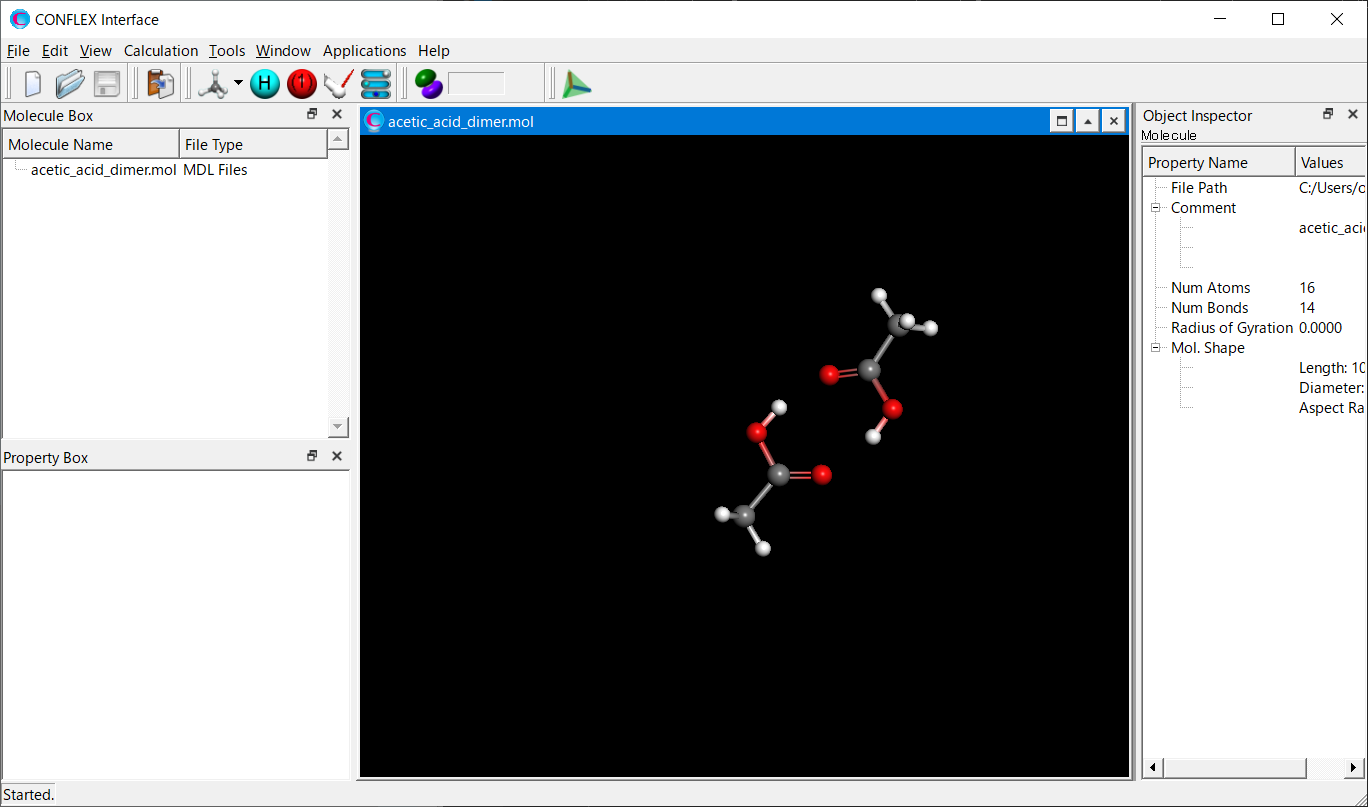
Select [CONFLEX] in Calculation menu, and click in the calculation setting dialog displayed.
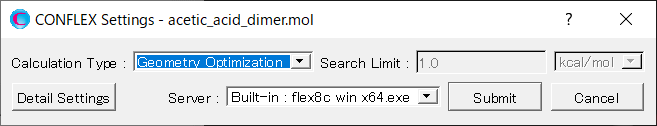
Next, in [General Settings] dialog on the detail setting dialog, select [Host Ligand Search] in the pull-down menu of [Calculation Type:].
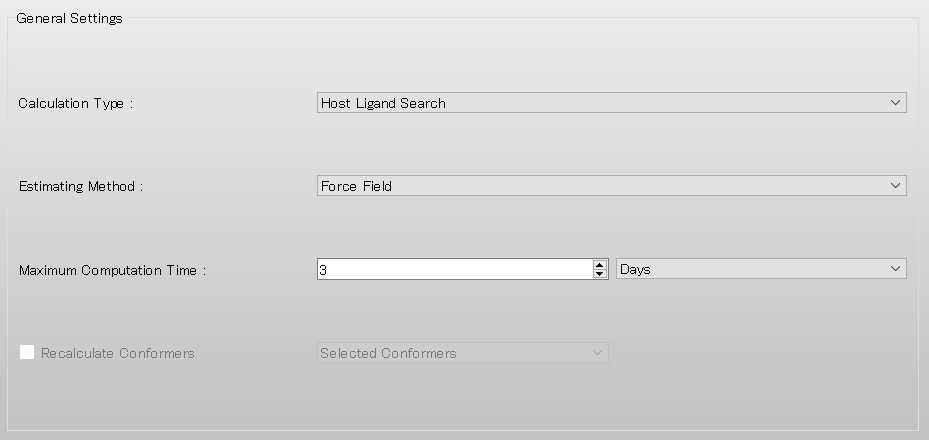
When the calculation setting is complete, click . The calculation will start.
[Execution by command line]
The calculation settings are defined by describing keywords in the acetic_acid_dimer.ini file.
acetic_acid_dimer.ini file
MMFF94S HLSEARCH
[HLSEARCH] means to perform a Host-Ligand coordination search.
[MMFF94s] means to use MMFF94s force field.
Store the two files of acetic_acid_dimer.mol and acetic_acid_dimer.ini in an one folder, and execute below command. The calculation will start.
C:\CONFLEX\bin\flex9a_win_x64.exe -par C:\CONFLEX\par acetic_acid_dimerenter
The above command is for Windows OS. For the other OS, please refer to [How to execute CONFLEX].
Calculation results
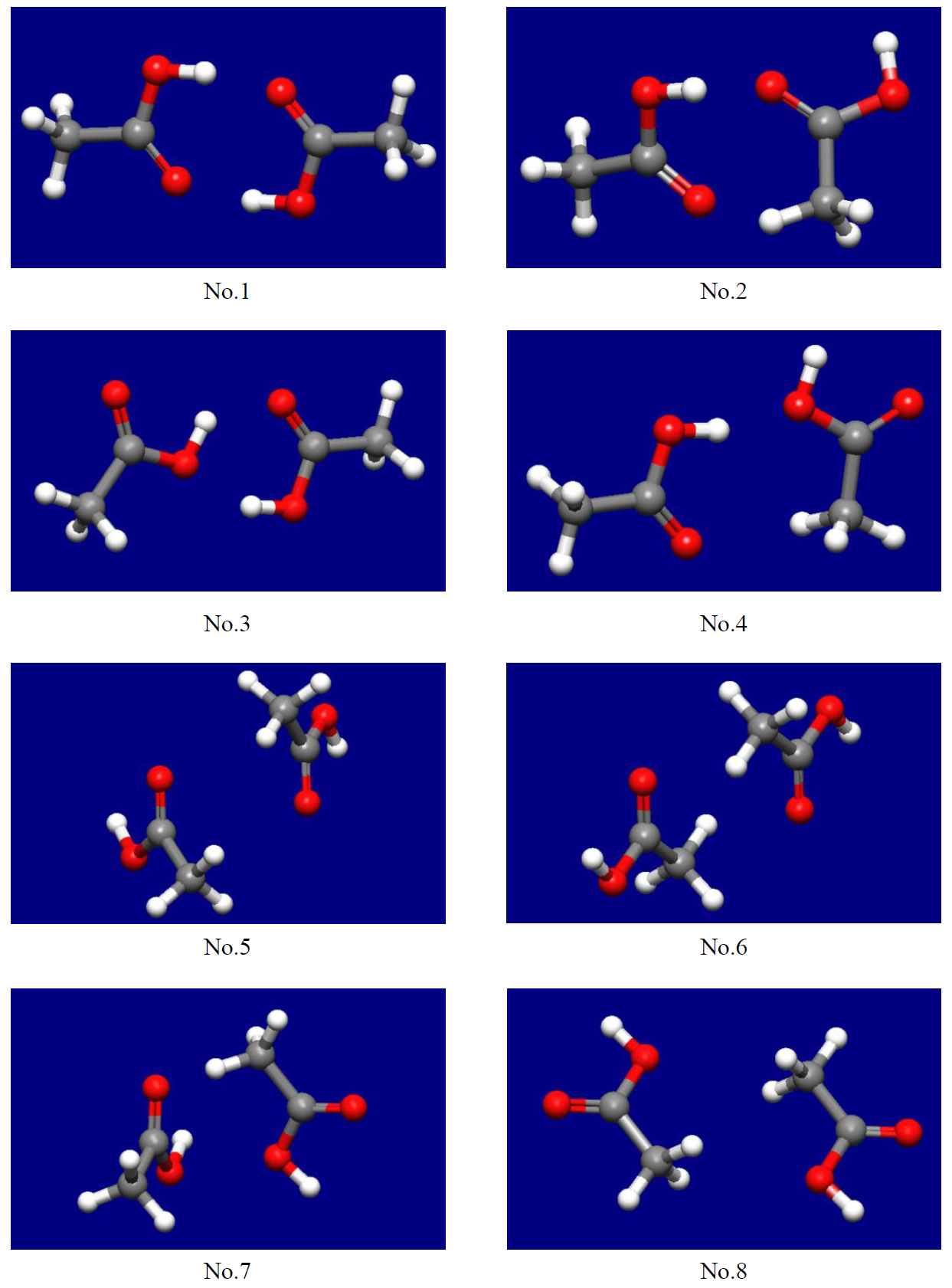
As the results, we can get 8 stable structures of the molecular complex (see below figure).
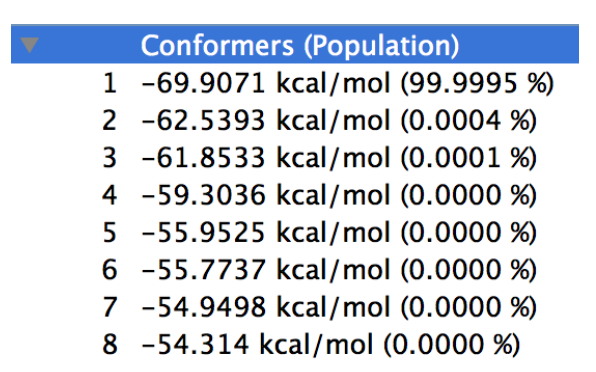
The energy list is shown in the Property Box of CONFLEX Interface like below figure.
About how to visualize the structures, please refer to [Visualization of calculation results].
[Coordination search of glucose and water molecules]
This section applies the Host-Ligand coordination search to a molecular complex of α-D-glucose and water molecules. Here, the α-D-glucose is the host molecule, and the water is the ligand molecule.
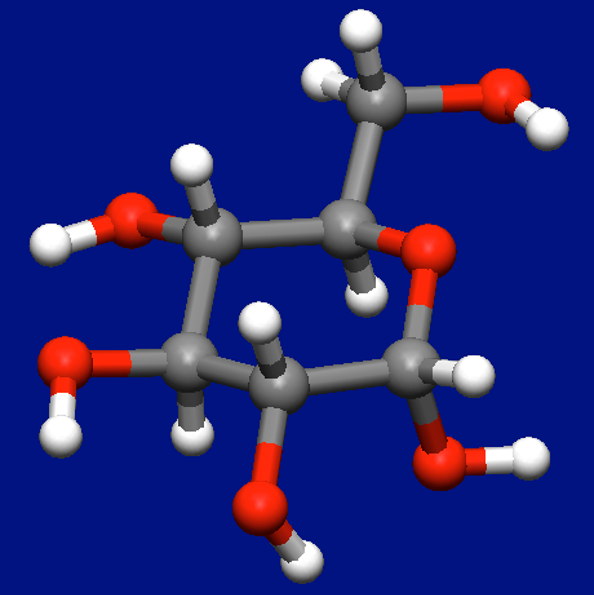
First, we obtain the most stable conformer of α-D-glucose (below figure) by a conformation search and MMFF94s force field.
Next, we create a molecular complex consists of α-D-glucose and water molecules by adding water molecule to the most stable conformer (see below figure).
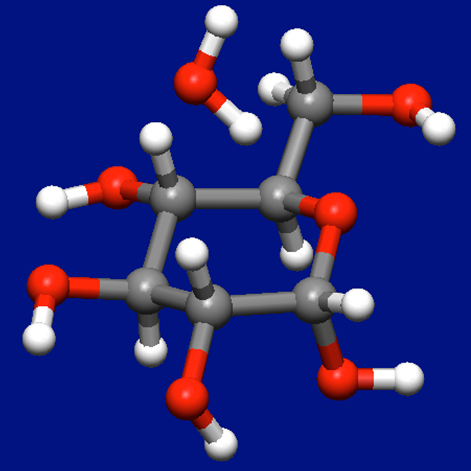
Structure data of the molecular complex for α-D-glucose and water molecules (aDglucose_H2O.mol)
aDglucose_H2O.mol
27 26 0 0 0 999 V2000
-0.5024 2.4148 0.6016 O 0 0 0 0 0
-0.8520 -1.0932 -0.5731 O 0 0 0 0 0
0.4519 -1.5744 -0.2774 C 0 0 0 0 0
-0.2020 1.2411 -0.1553 C 0 0 0 0 0
-1.1949 0.1125 0.1452 C 0 0 0 0 0
2.1431 1.8092 -0.2200 O 0 0 0 0 0
0.5330 -1.9764 1.0847 O 0 0 0 0 0
2.8319 -0.9820 -0.1321 O 0 0 0 0 0
-2.6186 0.5024 -0.2701 C 0 0 0 0 0
1.5391 -0.5233 -0.5592 C 0 0 0 0 0
1.2184 0.7799 0.1723 C 0 0 0 0 0
-3.5094 -0.5881 -0.0183 O 0 0 0 0 0
0.2794 2.9953 0.4978 H 0 0 0 0 0
0.6445 -2.4621 -0.8896 H 0 0 0 0 0
-0.2535 1.5201 -1.2154 H 0 0 0 0 0
-1.2141 -0.1177 1.2184 H 0 0 0 0 0
3.0267 1.3889 -0.1951 H 0 0 0 0 0
-0.0183 -2.7768 1.1469 H 0 0 0 0 0
2.6839 -1.4193 0.7318 H 0 0 0 0 0
-2.6702 0.7196 -1.3421 H 0 0 0 0 0
-2.9791 1.3731 0.2851 H 0 0 0 0 0
1.6027 -0.3262 -1.6358 H 0 0 0 0 0
1.3472 0.6668 1.2558 H 0 0 0 0 0
-3.0727 -1.3725 -0.4004 H 0 0 0 0 0
-0.3106 0.8234 -2.7522 O 0 0 0 0 0
-0.3290 0.0085 -2.2451 H 0 0 0 0 0
-0.9697 0.7822 -3.4490 H 0 0 0 0 0
1 4 1 0 0 0 0
1 13 1 0 0 0 0
2 3 1 0 0 0 0
2 5 1 0 0 0 0
3 7 1 0 0 0 0
3 10 1 0 0 0 0
3 14 1 0 0 0 0
4 5 1 0 0 0 0
4 11 1 0 0 0 0
4 15 1 0 0 0 0
5 9 1 0 0 0 0
5 16 1 0 0 0 0
6 11 1 0 0 0 0
6 17 1 0 0 0 0
7 18 1 0 0 0 0
8 10 1 0 0 0 0
8 19 1 0 0 0 0
9 12 1 0 0 0 0
9 20 1 0 0 0 0
9 21 1 0 0 0 0
10 11 1 0 0 0 0
10 22 1 0 0 0 0
11 23 1 0 0 0 0
12 24 1 0 0 0 0
25 26 1 0 0 0 0
25 27 1 0 0 0 0
M END
[Execution by Interface]
Open the aDglucose_H2O.mol file by CONFLEX Interface.
Select [CONFLEX] in Calculation menu, and click in the calculation setting dialog displayed.
Next, in [General Settings] dialog on the detail setting dialog, select [Host Ligand Search] in the pull-down menu of [Calculation Type:]. When you complete the setting, click on the detail setting dialog.
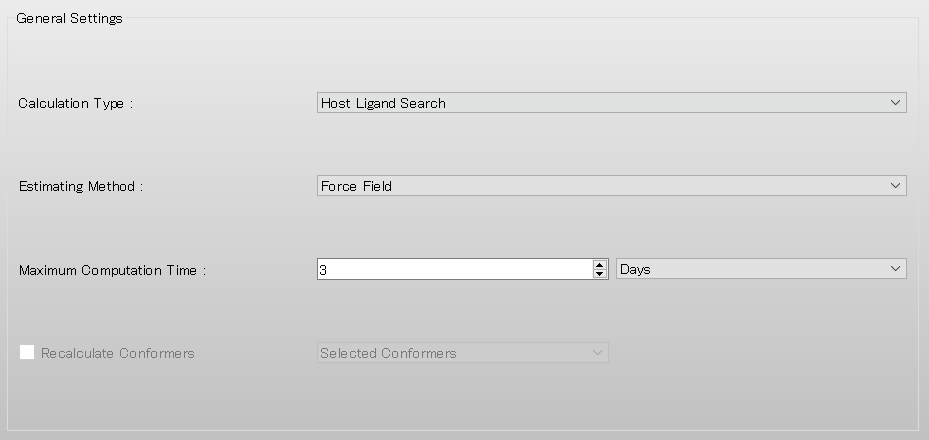
Add [OPT=GROUP] and [MOL_GROUP=(25,1)] to the dialog displayed.
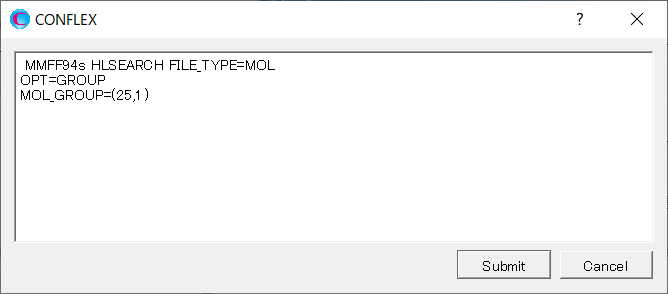
Here, the settings of [OPT=GROUP] and [MOL_GROUP=(25,1)] mean that the position and geometry of water molecule are optimized and those of α-D-glucose are fixed in the calculation.
About a geometry optimization with constraints, please refer to [Constraint by molecular object method].
When you complete the modifications, click . The calculation will start.
[Execution by command line]
The calculation settings are defined by describing keywords in the aDglucose_H2O.ini file.
aDglucose_H2O.ini file
HLSEARCH OPT=GROUP MOL_GROUP=(25,1)
[HLSEARCH] means to perform a Host-Ligand coordination search.
The settings of [OPT=GROUP] and [MOL_GROUP=(25,1)] mean that the position and geometry of water molecule are optimized and those of α-D-glucose are fixed in the calculation.
About a geometry optimization with constraints, please refer to [Constraint by molecular object method].
Store the two files of aDglucose_H2O.mol and aDglucose_H2O.ini in an one folder, and execute below command. The calculation will start.
C:\CONFLEX\bin\flex9a_win_x64.exe -par C:\CONFLEX\par aDglucose_H2Oenter
The above command is for Windows OS. For the other OS, please refer to [How to execute CONFLEX].
Calculation results
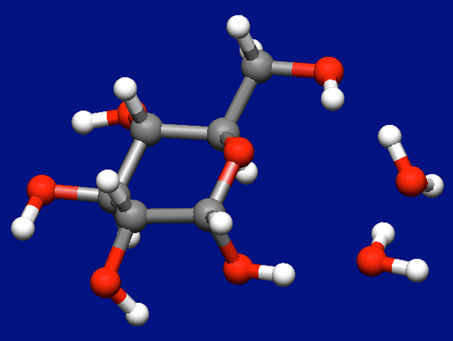
As the results, we can get 10 stable structures of the molecular complex of α-D-glucose and water molecules. The most stable structure is shown in the below figure.
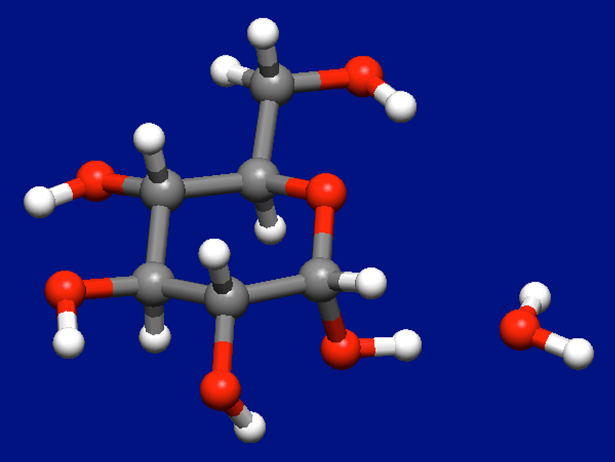
In case of two water molecules coordinate to the α-D-glucose
We add one water molecule to the most stable structure of α-D-glucose and water molecules shown above and perform the Host-Ligand coordination search once again.
Structure data
aDglucose_2H2O.mol
30 28 0 0 999 V2000
-1.7903 2.0810 -0.8582 O 0 0 0 0 0
0.9497 0.1820 0.7911 O 0 0 0 0 0
0.4899 -1.1464 0.5531 C 0 0 0 0 0
-1.1899 1.1508 0.0453 C 0 0 0 0 0
0.3377 1.1585 -0.0836 C 0 0 0 0 0
-3.1447 -0.2633 -0.0402 O 0 0 0 0 0
0.9130 -1.5822 -0.7345 O 0 0 0 0 0
-1.4750 -2.5911 0.2513 O 0 0 0 0 0
0.9177 2.5280 0.2908 C 0 0 0 0 0
-1.0411 -1.2797 0.6520 C 0 0 0 0 0
-1.7220 -0.2507 -0.2493 C 0 0 0 0 0
2.3453 2.4922 0.1999 O 0 0 0 0 0
-2.7454 1.8632 -0.8498 H 0 0 0 0 0
0.9541 -1.8120 1.2891 H 0 0 0 0 0
-1.4901 1.4462 1.0585 H 0 0 0 0 0
0.6456 0.9385 -1.1142 H 0 0 0 0 0
-3.3916 -1.2089 0.0143 H 0 0 0 0 0
1.8682 -1.7501 -0.6492 H 0 0 0 0 0
-0.9383 -2.8164 -0.5360 H 0 0 0 0 0
0.6697 2.7883 1.3250 H 0 0 0 0 0
0.5535 3.3193 -0.3704 H 0 0 0 0 0
-1.3717 -1.1301 1.6858 H 0 0 0 0 0
-1.5810 -0.5013 -1.3080 H 0 0 0 0 0
2.6160 1.6280 0.5609 H 0 0 0 0 0
3.5948 -1.8804 -0.5097 O 0 0 0 0 0
4.1240 -1.1431 -0.8632 H 0 0 0 0 0
4.2686 -2.5619 -0.3423 H 0 0 0 0 0
-0.2472 0.9616 3.3577 O 0 0 0 0 0
0.3575 0.6108 2.6999 H 0 0 0 0 0
-1.1224 1.0508 2.9734 H 0 0 0 0 0
1 4 1 0 0
1 13 1 0 0
2 3 1 0 0
2 5 1 0 0
3 7 1 0 0
3 10 1 0 0
3 14 1 0 0
4 5 1 0 0
4 11 1 0 0
4 15 1 0 0
5 9 1 0 0
5 16 1 0 0
6 11 1 0 0
6 17 1 0 0
7 18 1 0 0
8 10 1 0 0
8 19 1 0 0
9 12 1 0 0
9 20 1 0 0
9 21 1 0 0
10 11 1 0 0
10 22 1 0 0
11 23 1 0 0
12 24 1 0 0
25 26 1 0 0
25 27 1 0 0
28 29 1 0 0
28 30 1 0 0
M END
[Execution by Interface]
Open the aDglucose_2H2O.mol file by CONFLEX Interface.
Select [CONFLEX] in Calculation menu, and click in the calculation setting dialog displayed.
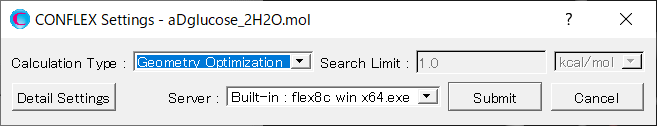
Next, in [General Settings] dialog on the detail setting dialog, select [Host Ligand Search] in the pull-down menu of [Calculation Type:].
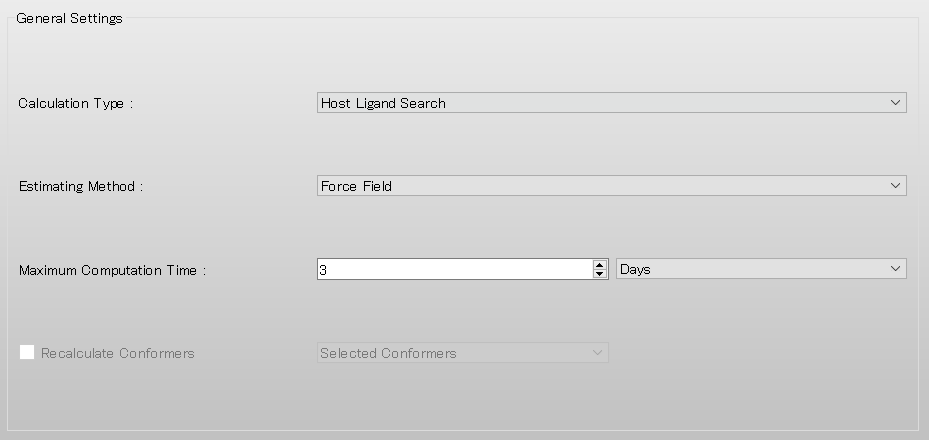
Next, settings of Host-Ligand coordination search are made in the [Host Ligand Search] dialog.
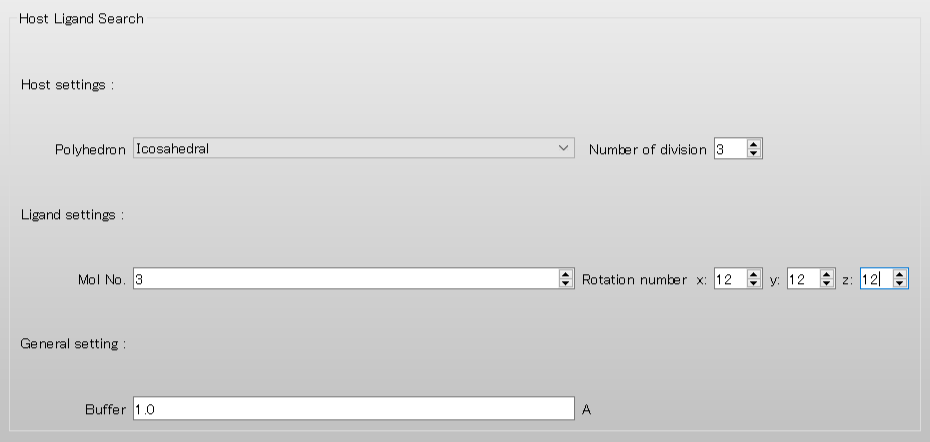
Set [Number of division] to 3. This setting provides the coordination search in detail by increasing points for arranging the ligand.
Set [Mol No.] of [Ligand settings:] to 3, to define the additional second water as the ligand.
Furthermore, set [Rotation number x:, y:, z:] to 12, respectively, to rotate the ligand by a step of 30 degrees.
When the calculation settings are complete, click .
Add [OPT=GROUP], [MOL_GROUP=(25,1)] and [MOL_GROUP=(28,1)] to the dialog displayed.
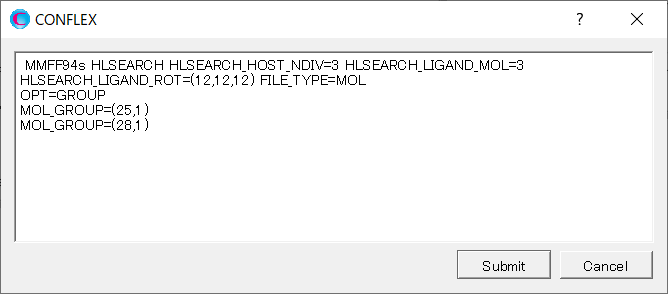
The settings of [OPT=GROUP], [MOL_GROUP=(25,1)] and [MOL_GROUP=(28,1)] mean that the position and geometry of water molecules are optimized and those of α-D-glucose are fixed in the calculation.
About a geometry optimization with constraints, please refer to [Constraint by molecular object method].
When you complete the modifications, click . The calculation will start.
[Execution by command line]
The calculation settings are defined by describing keywords in the aDglucose_2H2O.ini file.
aDglucose_2H2O.ini file
HLSEARCH OPT=GROUP MOL_GROUP=(25,1) MOL_GROUP=(28,1) HLSEARCH_HOST_NDIV=3 HLSEARCH_LIGAND_ROT=(12,12,12) HLSEARCH_LIGAND_MOL=3
Explanations of each keyword are shown below.
| Keyword | Explanation |
|---|---|
| HLSEARCH | Execute a Host-Ligand coordination search |
|
OPT=GROUP MOL_GROUP=(25,1) MOL_GROUP=(28,1) |
Position and geometry of water molecules are optimized and those of α-D-glucose are fixed in the calculation. |
| HLSEARCH_HOST_NDIV=3 | This setting provides the coordination search in detail by increasing points for arranging the ligand. |
| HLSEARCH_LIGAND_ROT=(12,12,12) | The ligand is rotated by a step of 30 degrees. |
| HLSEARCH_LIGAND_MOL=3 | The additional second water is defined as the ligand. |
Store the two files of aDglucose_2H2O.mol and aDglucose_2H2O.ini in an one folder, and execute below command. The calculation will start.
C:\CONFLEX\bin\flex9a_win_x64.exe -par C:\CONFLEX\par aDglucose_2H2Oenter
The above command is for Windows OS. For the other OS, please refer to [How to execute CONFLEX].
Calculation results
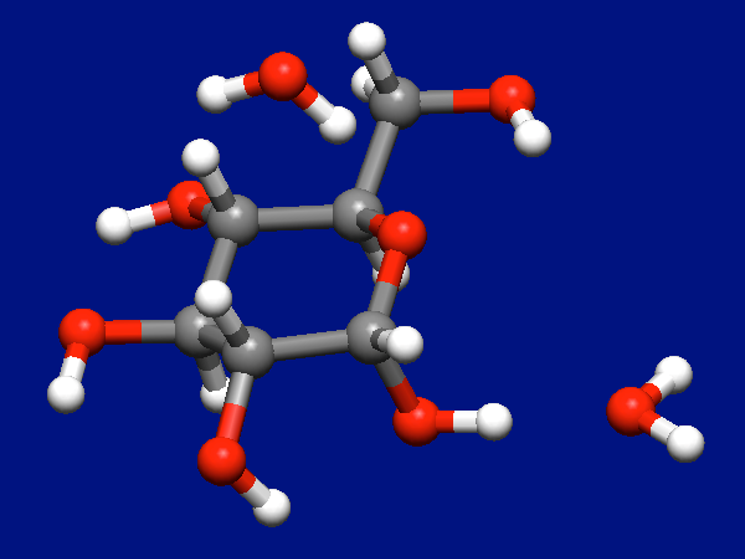
The most stable structure of α-D-glucose and two water molecules found by the search is shown below.